VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM) is a business continuity and disaster recovery solution that helps you plan, test, and run the recovery of virtual machines between a protected vCenter Server site and a recovery vCenter Server site1.
Overview
VMware Site Recovery Manager is an extension to VMware vCenter that provides disaster recovery, site migration, and non-disruptive testing capabilities to VMware customers. It is fully integrated with VMware vCenter Server and utilizes an HTML5 based “Clarity” UI.
Site Recovery Manager works in conjunction with various replication solutions including VMware vSphere Replication™ to automate the process of migrating, recovering, testing, re-protecting, and failing-back virtual machine workloads.
Site Recovery Manager servers coordinate the operations of the VMware vCenter Server™ at two sites. This is so that as virtual machines at the protected site are shut down, copies of these virtual machines at the recovery site startup. By using the data replicated from the protected site these virtual machines assume responsibility for providing the same services.
Migration of protected inventory and services from one site to the other is controlled by a recovery plan that specifies the order in which virtual machines are shut down and started up, the resource pools to which they are allocated, and the networks they can access. Site Recovery Manager enables the testing of recovery plans, using a temporary copy of the replicated data, and isolated networks in a way that does not disrupt ongoing operations at either site. Multiple recovery plans can be configured to migrate individual applications and entire sites providing finer control over what virtual machines are failed over and failed back. This also enables flexible testing schedules.
Site Recovery Manager extends the feature set of the virtual infrastructure platform to provide for rapid business continuity through partial or complete site failures.
Here are some key points about SRM:
- Planned Migration:
- During a planned migration, SRM synchronizes the virtual machine data from the protected site to the recovery site.
- It attempts to gracefully shut down the protected virtual machines and performs a final synchronization to prevent data loss.
- Afterward, it powers on the virtual machines at the recovery site.
- If errors occur during migration, the plan stops for resolution before rerunning.
- You can reprotect the virtual machines after successful migration.
- Disaster Recovery:
- In a disaster recovery scenario, SRM first attempts storage synchronization.
- If successful, it uses the synchronized storage state to recover virtual machines on the recovery site.
- The recovery is based on the most recent available state, according to the recovery point objective (RPO) set during replication configuration.
- If SRM cannot shut down virtual machines on the protected site, it still powers on the copies at the recovery site.
- In case the protected site comes back online after disaster recovery, SRM detects this and allows you to run the plan again to power off the virtual machines on the protected site.
- This ensures consistency and enables subsequent reprotect operations.
Features and Benefits of Site Recovery Manager
- Application-agnostic protection eliminates the need for app-specific point solutions
- Automated orchestration of site failover and failback with a single-click reduces recovery times
- Frequent, non-disruptive testing of recovery plans ensures highly predictable recovery objectives
- Centralized management of recovery plans from the HTML5 UI replaces manual runbooks
- Planned migration workflow enables disaster avoidance and data center mobility
- VMware vSAN integration reduces the DR footprint through hyper-converged, software-defined storage
- Supports multiple versions of vCenter enabling flexible pairing and upgrading
- vSphere Replication integration delivers VM-centric, replication that eliminates dependence on storage
Terminology
Recovery time objective (RTO): Targeted amount of time a business process should be restored after a disaster or disruption to avoid unacceptable consequences associated with a break in business continuity.
Recovery point objective (RPO): Maximum age of files recovered from backup storage for normal operations to resume if a system goes offline because of a hardware, program, or communications failure.
Protected site: Site that contains protected virtual machines.
Recovery site: Site where protected virtual machines are recovered in the event of a failover.
NOTE: It is possible for the same site to serve as a protected site and recovery site when replication is occurring in both directions and Site Recovery Manager is protecting virtual machines at both sites.
Architectural Overview
Site Recovery Manager is deployed in a paired configuration, for example, protected site and recovery site.
Site Recovery Manager is deployed in a paired configuration, for example, a protected site and a recovery site. The Site Recovery Manager software is deployed as an appliance at both sites. It supports multiple versions of vCenter at either site. There must be one or more vSphere hosts running version 6.5 or higher at each site. See the Compatibility Matrixes for Site Recovery Manager for specific details
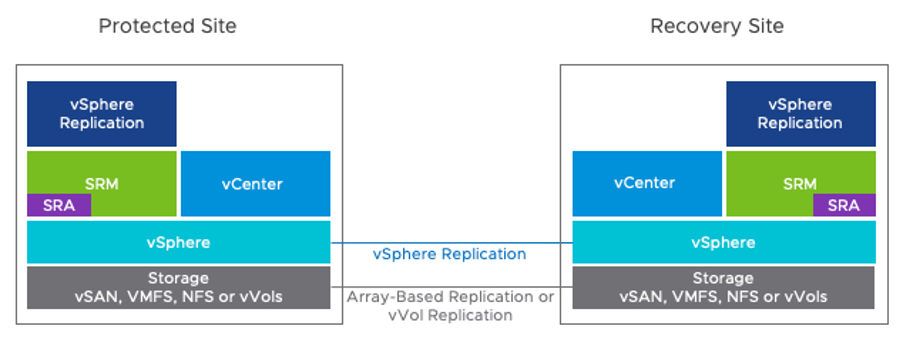
Note: Here we are not disclosing any information regarding Array-Based Replication or vVol Replication in this Blog as we are supporting only vSphere Replication to our Customer.
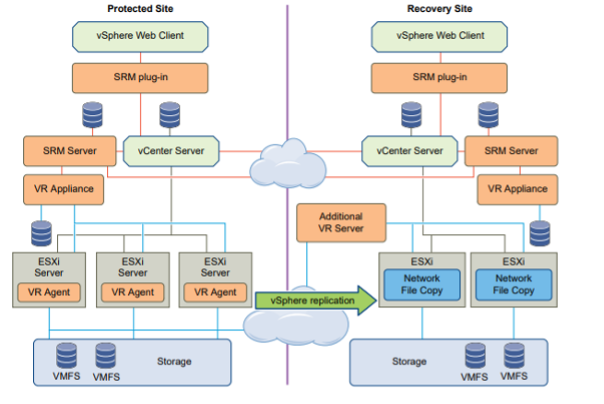
Using vSphere Replication with Site Recovery Manager
Site Recovery Manager can use vSphere Replication to replicate data to servers at the recovery site.
vSphere Replication does not require storage arrays. The vSphere Replication storage replication source and target can be any storage device, including, but not limited to, storage arrays.
You can configure vSphere Replication to regularly create and retain snapshots of protected virtual machines on the recovery site. Taking multiple point-in-time (PIT) snapshots of virtual machines allows you to retain more than one replica of a virtual machine on the recovery site. Each snapshot reflects the state of the virtual machine at a certain point in time. You can select which snapshot to recover when you use vSphere Replication to perform a recovery.
Site Recovery Manager Architecture with vSphere Replication
Pros & Cons of Site Recovery Manager
Pros:
- Automated Recovery: VMware SRM offers automated recovery, streamlining the process and reducing manual intervention.
- Simplified Management: It provides a centralized interface for configuring, testing, and executing disaster recovery plans across multiple sites, making management easier even for many sites2.
- Integration: VMware SRM integrates well with other VMware technologies and architectures.
- Non-Disruptive Testing: You can conduct tests during business hours without disruptions3.
Cons:
- Cost: Licensing and implementation costs can be significant.
- Complexity: Setting up and configuring SRM can be complex, especially for organizations with diverse environments.
- Resource Overhead: SRM requires additional resources (such as storage and compute) for replication and failover processes.
Conclusion:
In today’s fast-paced business environment, ensuring continuous availability and rapid recovery from disasters is critical. VMware SRM offers a proven and effective solution, enabling organizations to protect their investments and maintain operational resilience. Whether dealing with planned maintenance or unexpected outages, SRM provides the tools needed to keep your business running smoothly.
By leveraging VMware SRM, organizations can achieve higher levels of reliability and assurance, knowing that their critical systems and data are protected and recoverable. Implementing SRM as part of your disaster recovery strategy is a smart investment in your organization’s future stability and success.




